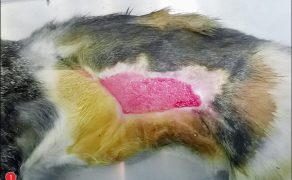
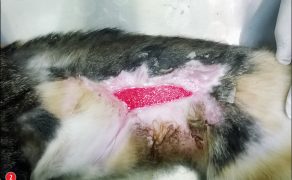
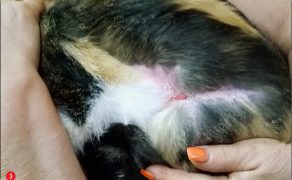
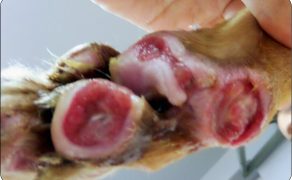
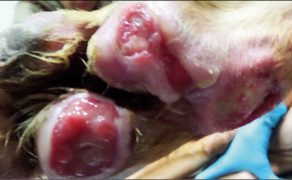
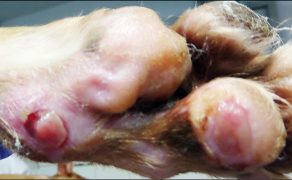
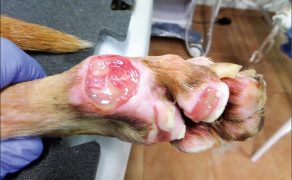
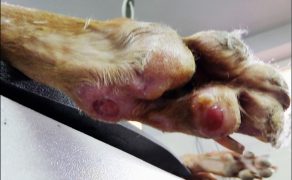
Zastosowanie czynników wzrostu w gojeniu dużych ubytków skórnych i ran przewlekłych u zwierząt towarzyszących
Piśmiennictwo
- Barrientos S., Stojadinovic O., Golinko M.S., Brem H., Tomic-Canic M.: Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. „Wound Repair Regen.”, 16 (2008), 585-601.
- Freedberg I.M., Tomic-Canic M., Komine M., Blumenberg M.: Keratins and the keratinocyte activation cycle. „J Invest Dermatol”, 2001; 116: 633-40.
- Hantash B.M., Zhao L., Knowles J.A., Lorenz H.P.: Adult and fetal wound healing. „Front Biosci”, 2008; 13: 51-61.
- Martin P.: Wound healing – aiming for perfect skin regeneration. „Science”, 199; 276: 75-81.
- Santoro M.M., Gaudino G.: Cellular and molecular facets of keratinocyte reepithelization during wound healing. „Exp. Cell Res.”, 2005; 304: 274-286.
- Atala A., Lanza R., Thomson J.A., Nerem R.: Principles of Regenerative Medicine. Elsevier, New York 2011.
- Fan Q., Yee C.L., Ohyama M., Tock C., Zhang G., Darling T.N., Vogel J.C.: Bone marrow-derived keratinocytes are not detected in normal skin and only rarely detected in wounded skin in two different murine models. „Exp. Hematol.”, 2006; 34: 672-679.
- Werner S., Grose R.: Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. „Physiol. Rev.”, 2003; 83: 835-870.
- Lanza R., Langer R., Vacanti J.: Principles of Tissue Engineering. Elsevier, 2000.
- Pierce G.F., Tarpley J.E., Tseng J., Bready J., Chang D., Kenney W.C., Rudolph R., Robson M.C., Vande Berg J., Reid P.: Detection of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-AA in actively healing human wounds treated with recombinant PDGF-BB and absence of PDGF in chronic non-healing wounds. „J. Clin. Invest.”, 1995; 96: 1336-1350.
- Jinnin M., Ihn H., Mimura Y., Asano Y., Yamane K., Tamaki K.: Regulation of fibrogenic/fibrolytic genes by platelet-derived growth factor C, a novel growth factor, in human dermal fibroblasts. ”J Cell Physiol”, 2005; 202: 510.
- Mast B.A., Schultz G.S.: Interactions of cytokines, growth factors, and proteases in acute and chronic wounds. „Wound Repair Regen”, 1996; 4: 411-20.
- Brown G.L., Curtsinger L., Brightwell J.R., Ackerman D.M., Tobin G.R., Polk H.C. Jr., George-Nascimento C., Valenzuela P., Schultz G.S.: Enhancement of epidermal regeneration by biosynthetic epidermal growth factor. „J Exp Med” 1986; 163: 1319-24.
- Brown G.L., Curtsinger L.J., White M., Mitchell R.O., Pietsch J. ,Nordquist R., von Fraunhofer A., Schultz G.S.: Acceleration of tensile strength of incisions treated with EGF and TGF-beta. „Ann Surg”, 1988; 208: 788-94.
- Kim I., Mogford J.E., Chao J.D., Mustoe T.A.: Wound epithelialization deficits in the transforming growth factor alpha knockout mouse. „Wound Repair Regen”, 2001; 9: 386-90.
- Wood L.C., Elias P.M., Calhoun C., Tsai J.C., Grunfeld C., Feingold K.R:. Barrier disruption stimulates interleukin-1 alpha expression and release from a pre-formed pool in murine epidermis. „J Invest Dermatol”, 1996; 106: 397-403.
- Ornitz D.M.: FGFs, heparan sulfate and FGFRs: complex interactions essential for development. „Bioessays”, 2000; 22: 108-12.
- Powers C.J., McLeskey S.W., Wellstein A.: Fibroblast growth factors, their receptors and signaling. „Endocr Relat Cancer”, 2000; 7: 165-97.
- Sogabe Y., Abe M., Yokoyama Y., Ishikawa O.: Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates human keratinocyte motility by Rac activation. „Wound Repair Regen”, 2006; 14: 457-62.
- Sasaki T.: The effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and doxorubicin on cultured human skin fibroblasts: relevance to wound healing. „J Dermatol”, 1992; 19: 664-6.
- Robson M.C.: The role of growth factors in the healing of chronic wounds. „Wound Repair Regen”, 1997; 5: 12-7.
- Robson M.C., Phillips L.G., Lawrence W.T., Bishop J.B., Youngerman J.S., Hayward P.G., Broemeling L.D., Heggers J.P.: The safety and effect of topically applied recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor on the healing of chronic pressure sores. „Ann Surg”, 1992; 216: 401-408.
- Friedlander M., Brooks P.C., Shaffer R.W., Kincaid C.M., Varner J.A., Cheresh D.A.: Definition of 2 angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha(V) integrins. „Science”, 1995; 270: 1500-1502.
- Clark RAF: The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair. 2nd ed. New York: Plenum Press, 1996.
- Riedel K., Riedel F., Goessler U.R., Germann G., Sauerbier M.: Tgf-beta antisense therapy increases angiogenic potential in human keratinocytes in vitro. „Arch Med Res”, 2007; 38: 45-51.
- White L.A., Mitchell T.I., Brinckerhoff C.E.: Transforming growth factor beta inhibitory element in the rabbit matrix metalloproteinase-1 (collagenase-1) gene functions as a repressor of constitutive transcription. „Biochim Biophys Acta”, 2000; 1490: 259-68.
- Cordeiro M.F., Reichel M.B., Gay J.A., D’Esposita F., Alexander R.A., Khaw P.T.: Transforming growth factor-beta1,-beta2, and -beta3 in vivo: effects on normal and mitomycin C-modulated conjunctival scarring. „Invest Ophthalmol VisSci” 1999; 40: 1975-82.
- Shah M., Foreman D.M., Ferguson M.W.: Neutralisation of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 or exogenous addition of TGF-beta 3 to cutaneous rat wounds reduces scarring. „J Cell Sci”, 1995; 108 (Pt 3): 985-1002.
- Tyrone J.W., Marcus J.R., Bonomo S.R., Mogford J.E., Xia Y,, Mustoe T.A.: Transforming growth factor beta3 promotes fascial wound healing in a new animal model. „Arch Surg”, 2000; 135: 1154-9.
- Bhansali A., Venkatesh S., Dutta P., Dhillon M.S., Das S., Agrawal A.: Which is the better option: recombinant human PDGF-BB 0.01% gel or standard wound care, in diabetic neuropathic large plantar ulcers off-loaded by a customized contact cast? „Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.”, 2009; 83: 13-16.
- Hong J.P., Jung H.D., Kim Y.W.: Recombinant human epidermal growth factor (EGF) to enhance healing for diabetic foot ulcers. „Ann. Plast. Surg.”, 2006; 56: 394-398.
- Roubelakis M.G., Trohatou O., Roubelakis A., Mili E., Kalaitzopoulos I., Papazoglou G., Pappa K.I., Anagnou N.P.: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) promotes fetal mesenchymal stem/stromal cell migration and wound healing process. „Stem Cell Rev.”, 2014; 10: 417-428.
- Atala A., Lanza R., Thomson J.A., Nerem R.: Principles of Regenerative Medicine. Elsevier, New York 2011.
- White L.A., Mitchell T.I., Brinckerhoff C.E.: Transforming growth factor beta inhibitory element in the rabbit matrix metalloproteinase-1 (collagenase-1) gene functions as a repressor of constitutive transcription. „Biochim Biophys Acta”, 2000; 1490: 259-68.
- Chen S.M., Ward S.I., Olutoye O.O., Diegelmann R.F., Kelman Cohen I.: Ability of chronic wound fluids to degrade peptide growth factors is associated with increased levels of elastase activity and diminished levels of proteinase inhibitors. „Wound Repair Regen”, 1997; 5: 23-32.
- Bernabei R., Landi F., Bonini S., Onder G., Lambiase A., Pola R., Aloe L.: Effect of topical application of nerve-growth factor on pressure ulcers. „Lancet”, 1999; 354: 307.
- Lewin G.R., Mendell L.M: Nerve growth factor and nociception. „Trends Neurosci”, 16: 353-359, 1993.
- Mann A., Breuhahn K., Schirmacher P., Blessing M:. Keratinocyte-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor accelerates wound healing: stimulation of keratinocyte proliferation, granulation tissue formation and vascularization. „J Invest Dermatol”, 2001; 117: 1382-90.
- Gough A., Clapperton M., Rolando N., Foster A..V, Philpott- Howard J., Edmonds M.E.: Randomised placebo-controlled trial of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in diabetic foot infection. „Lancet”, 1997; 350: 855-9.
- Bussolino F., Wang J.M., Defilippi P., Turrini F., Sanavio F., Edgell C.J., Aglietta M., Arese P., Mantovani A.: Granulocyteand granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factors induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. „Nature”, 1989; 337: 471-3.
lek. wet. Aneta Bocheńska
Uniwersyteckie Centrum Medycyny Weterynaryjnej UJ-UR
al. Mickiewicza 21 31-120 Kraków
Galeria
Mogą zainteresować Cię również
Znajdź swoją kategorię
2843 praktycznych artykułów - 324 ekspertów - 23 kategorii tematycznych
Weterynaria w Terenie

Mykotoksyny – ukryty wróg w hodowli bydła mlecznego
Zatrucie mykotoksynami – objawy i diagnostyka Objawy kliniczne sugerujące zatrucie mykotoksynami u bydła mlecznego mogą być niespecyficzne i często nakładać się na inne problemy zdrowotne lub środowiskowe na fermie. Ważne, aby zrozumieć, że inne czynniki chorobotwórcze, złe warunki dobrostanowe czy niewłaściwe żywienie mogą potęgować efekty działania mykotoksyn i nawet mniejsza kontaminacja pasz w połączeniu z […]

Kulawizna u bydła mlecznego (choroba Mortellaro). Skuteczne zwalczanie zapalenia skóry palca dzięki naturalnemu rozwiązaniu
Biodevas Laboratoires opracowała PIETIX – rozwiązanie w 100% naturalne, mające na celu zwalczenie zapalenia skóry palca u bydła mlecznego.

Czynniki wpływające na kolonizację mikrobiomu i dojrzałość układu pokarmowego prosiąt oraz jego prawidłowe funkcjonowanie
Równowaga elektrolitowa Do jelit warchlaków codziennie trafia od 8 do 10 l płynu, a większość wchłaniania wody następuje w jelicie cienkim (10). Wchłanianie i wydzielanie w błonie śluzowej jelit zachodzi jednocześnie, w zależności od polarności komórek nabłonkowych, i pomaga utrzymać potencjał błonowy, żywotność komórek, odpowiednie wchłanianie składników odżywczych i regulację metabolizmu drobnoustrojów (78). Wchłanianie wody […]

Opieka stomatologiczna nad starszymi końmi
Braki w uzębieniu U starszych koni dość częstym problemem są braki w uzębieniu. Powodem mogą być ekstrakcje we wcześniejszym okresie życia, diastemy i choroby przyzębia doprowadzające do rozchwiania i wypadania lub po prostu zużycie się zęba. O ile brak jednego zęba policzkowego nie wpływa znacząco na rozcieranie paszy, o tyle brak 3-4 zębów już bardzo […]

Praktyka w terenie – jak zabezpieczyć się na wypadek stanów zagrożenia życia lub zdrowia zwierzęcia
Piśmiennictwo mec. Anna SłowińskaVox Poland Pomoc PrawnaSzczecin Facebook0Tweet0LinkedIn0

Wiek ma ogromne znaczenie podczas stawiania diagnozy
Lek. wet. Justyna Domagała tytuł inżyniera zootechniki uzyskała w 2016 r., a tytuł lekarza weterynarii – w 2019 r. na Uniwersytecie Przyrodniczym we Wrocławiu. Po studiach swoją wiedzę poszerzała podczas stażu w Szpitalu dla Koni Equivet, w którym później uzyskała zatrudnienie. W latach 2021-2024 swoją pracę skupiała na internistycznym leczeniu koni oraz pogłębianiu wiedzy na […]
Echa 32. Kongresu Bujatrycznego w Cancun
Profilaktyka Kongres był również okazją do zaprezentowania kilku przełomowych produktów immunologicznych, które mają szansę wprowadzić na nowe tory prewencję znanych od lat jednostek chorobowych, sprawiających wiele kłopotów z punktu widzenia odchowu cieląt czy rozrodu. Mowa tu konkretnie o trzech nowych szczepionkach mających zastosowanie w profilaktyce Mycoplasma bovis, Cryptosporidium parvum czy wirusowej biegunki bydła (BVD). Nie […]