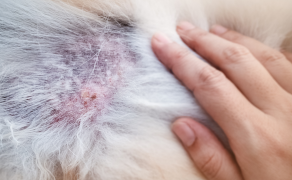
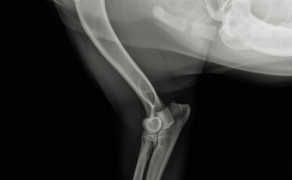
Czy coroczne szczepienia mogą być czynnikiem ryzyka dla rozwoju przewlekłej choroby nerek u kotów?
Piśmiennictwo
- Bartlett P.C., Van Buren J.W., Bartlett A.D. et al.: Case-control study of risk factors associated with feline and canine chronic kidney disease. „Vet Med Int”, 2010, 9, 1-9.
- Conroy M., Brodbelt D.C., O’Neill D., Chang Y.M., Elliott J.: Chronic kidney disease in cats attending primary care practice in the UK: VetCompass™ study. „Vet Rec”, 2019, 27, 184 (17), 526.
- Finch N.C., Syme H.M., Elliott J.: Risk Factors for Development of Chronic Kidney Disease in Cats. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2016, 30, 602-610.
- Furuya T., Wachi A., Sassa Y. et al.: Quantitative PCR detection of feline morbillivirus in cat urine samples. „J Vet Med Sci”, 2016, 77, 1701-1703.
- Greene J.P., Lefebvre S.L., Wang M. et al.: Risk factors associated with the development of chronic kidney disease in cats evalu-ated at primary care veterinary hospitals. „J Am Vet Med Assoc”, 2014, 244, 320-327.
- Greiner M., Wolf G., Hartmann K.: A retrospective study of the clinical presentation of 140 dogs and 39 cats with bacteraemia. „J Small Anim Pract”, 2008, 49, 378-383.
- Lappin M.R., Jensen W.A., Jensen T.D. et al.: Investigation ofthe induction of antibodies against Crandell-Rees feline kidney cell lysates and feline renal cell lysates after parenteral administration of vaccines against feline viral rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, and pan-leukopenia in cats. „Am J Vet Res”, 2005, 66, 506-511.
- Lappin M.R., Basaraba R.J., Jensen W.A.: Interstitial nephritisin cats inoculated with Crandell Rees feline kidney cell lysates. „J Feline Med Surg”, 2006, 8, 353-356.
- McCallum K., Stubbs S., Hope N. et al.: Detection and seroprevalence of morbillivirus and other paramyxoviruses in geriatric cats with and without evidence of azotemic chronic kidney disease. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2018, 32 (3), 1100-1108.
- Roura X.: Risk factors in dogs and cats for development of chronic kidney disease. IRIS webpage: http://www.iris-kidney.com/education/risk_factors.html.
- Sharp C., Nambulli S., Acciardo A. et al.: Chronic Infection of Domestic Cats with Feline Morbillivirus. „United States Emerg Infect Dis”, 2016, 22 (4), 760-762.
- Stranieri A., Lauzi S., Dallari A.: Feline morbillivirus in Northern Italy: prevalence in urine and kidneys with and without renal disease. „Vet Microbiol”, 2019, 233, 133-139.
- Tushika B., Pandey A., Deepa D., Asthana A.: C-reactive protein (CRP) and its association with periodontal disease: a brief review. „J Clin Diagn Res”, 2014, 8 (7), 21-24.
- Woo P.C., Lau S.K., Wong B.H. et al.: Feline morbillivirus, a previously undescribed paramyxovirus associated with tubulointerstitial nephritis in domestic cats. „Proc Natl Acad Sci USA”, 2012, 109, 5435-5440.
- Whittemore J.C., Hawley J.R., Jensen W.A. et al.: Antibodiesagainst Crandell Rees feline kidney (CRFK) cell line antigens,alpha-enolase, and annexin A2 in vaccinated and CRFK hyper-inoculated cats. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2010, 24, 306-313,16.
dr n. wet. Magdalena KalwasŚliwińska
Katedra Chorób Małych Zwierząt
z Kliniką
Wydział Medycyny Weterynaryjnej
SGGW w Warszawie
ul. Nowoursynowska 159
02-776 Warszawa
Galeria
Mogą zainteresować Cię również
Znajdź swoją kategorię
2634 praktycznych artykułów - 324 ekspertów - 22 kategorii tematycznych
Weterynaria w Terenie

Kiedy warto zlecić rozmaz krwi u koni?
Po drugie, w rozmazie możliwe jest postawienie podejrzenia aglutynacji erytrocytów, sugerującej immunohemolityczne tło niedokrwistości – IMHA (ryc. 3). Weryfikacja występowania aglutynacji następuje w teście aglutynacji szkiełkowej. Niedokrwistości immunohemolitycznej może także towarzyszyć obecność sferocytów (choć rzadko spotykana u koni). W przypadku hemolizy na tle uszkodzeń oksydacyjnych erytrocytów (np. w przypadku zatruć liśćmi czerwonego klonu lub DMSO) […]

Ostertagioza bydła – nowe aspekty epizootiologiczne
Badania częstości występowania zarażenia Ostertagia ostertagi przeprowadzono w latach 2014-2016 w Zakładzie Chorób Zakaźnych Zwierząt i Administracji Weterynaryjnej Wydziału Medycyny Weterynaryjnej we Wrocławiu w 476 stadach bydła mlecznego zlokalizowanych na terenie Polski, w których nie prowadzono profilaktyki przeciwko pasożytom żołądkowo-jelitowym. Celem podjętych badań było rozpoznanie, co do częstotliwości i lokalizacji na obszarze Polski, występowania w […]

Rozpoznawanie ciąży u świń w warunkach terenowych
Korzyści wynikające z zastosowania USG Poważną zaletą USG jest możliwość bardzo wczesnej i pewnej diagnostyki ciąży. Może to mieć znaczenie szczególnie w dużych fermach, gdzie wcześniejsze, o 7-14 dni (w porównaniu do detektorów wód płodowych), rozpoznanie braku ciąży oraz w porę wprowadzone postępowanie zaradcze może dać ogromne oszczędności przez znaczne obniżenie liczby nieproduktywnych dni oraz […]

Kiedy warto zlecić rozmaz krwi u koni?
Po drugie, w rozmazie możliwe jest postawienie podejrzenia aglutynacji erytrocytów, sugerującej immunohemolityczne tło niedokrwistości – IMHA (ryc. 3). Weryfikacja występowania aglutynacji następuje w teście aglutynacji szkiełkowej. Niedokrwistości immunohemolitycznej może także towarzyszyć obecność sferocytów (choć rzadko spotykana u koni). W przypadku hemolizy na tle uszkodzeń oksydacyjnych erytrocytów (np. w przypadku zatruć liśćmi czerwonego klonu lub DMSO) […]
Wskazówki na wypadek widocznego niepowodzenia terapii antybiotykowej. Kryteria skutecznej terapii oraz kluczowe pytania jako 5 kroków drzewa analitycznego
Czynniki powiązane z użyciem antybiotyku w terapii: Czy wybór antybiotyku opierał się na badaniach klinicznych i dodatkowych (diagnoza, antybiogram)? Sprawdź odpowiedź na pytanie 3. Farmakokinetyka/farmakodynamika wybranego antybiotyku? Koncentracja i czas działania antybiotyku w zakażonej tkance a efektywność w stosunku do czynnika bakteryjnego wywołującego chorobę (spektrum działania antybiotyku, wrażliwość z antybiogramu – odpowiedzi na pytanie 3.). […]

Czarno na białym – mastitis okiem praktyka – rozmowa z dr. n. wet. Sebastianem Smulskim
Rozmowa z dr. n. wet. Sebastianem Smulskim, pracownikiem Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczego w Poznaniu, specjalistą w dziedzinie profilaktyki i leczenia mastitis u krów, który w swoich badaniach zgłębia tematykę zapalenia gruczołu mlekowego u bydła, zarówno w aspekcie naukowym, jak i praktycznym. Większość zapaleń gruczołu mlekowego ma etiologię bakteryjną. Dlaczego, pomimo rozwoju mikrobiologii, medycyny weterynaryjnej i prowadzonych badań, […]

XVIII FORUM ZOOTECHNICZNO-WETERYNARYJNE: NOWE HORYZONTY W ROZRODZIE ZWIERZĄT
Na Uniwersytecie Przyrodniczym w Poznaniu w dniach 18-19 kwietnia br. odbyło się XVIII Forum Zootechniczno-Weterynaryjne pod hasłem „Rozród zwierząt w dobie selekcji genomowej”. To wydarzenie zgromadziło liczne grono lekarzy weterynarii oraz hodowców, by omówić najnowsze osiągnięcia w dziedzinie hodowli i rozrodu zwierząt. Organizacja Forum była wspólnym przedsięwzięciem Poznańskiego Koła Polskiego Towarzystwa Zootechnicznego, Wielkopolskiego Oddziału Polskiego […]