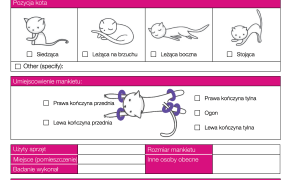
Pomiar ciśnienia krwi u psów i kotów
Piśmiennictwo
- Garner D., Laks M.M.: New implanted chronic catheter device for determining blood pressure and cardiac output in conscious dog. „Am J Physiol”, 1985, 249, H681-H684, 3.
- Scully P., Chan P.S., Cervoni P.: A method of measuring direct arterial blood pressure. „Canine Pract”, 1983, 10, 24-33.
- Vachon C., Belanger M.C., Burns P.M.: Evaluation of oscillometric andDoppler ultrasonic devices for blood pressure measurements in anesthetized and conscious dogs. „Res Vet Sci”, 2014, 97, 111-117.
- Bosiack A.P. et al.: Comparison of ultrasonic Doppler flow monitor, oscillometric, anddirect arterial blood pressure measurements in ill dogs. „J Vet EmergCrit Care (San Antonio)”, 2010, 20, 207-215.12.
- Haberman C.E. et al.: Evaluation of oscil-lometric and Doppler ultrasonic methods of indirect blood pressureestimation in conscious dogs. „Can J Vet Res”, 2006, 70, 211-217.
- Binns S.H. et al.: Doppler ultrasono-graphic, oscillometric sphygmom anometric, and photoplethysmo-graphic techniques for noninvasive blood pressure measurement inanesthetized cats. „J Vet Intern Med”, 1995, 9, 405-414.
- Gouni V. et al.: Influence of the observer’s level of experience on systolic and diastolic arterial blood pressure measurements using Doppler ultra sonography in healthy conscious cats. „J Feline Med Surg”, 2015, 17, 94-100.
- Williams T.L., Elliott J., Syme H.M.: Measurement of systolic blood pressure (SBP) in cats by the indirect Doppler technique is not altered by the use of headphones. „ECVIM Congress”, 2010.
- Bodey A.R., Michell A.R.: Epidemiological study of blood pressure indomestic dogs. „J Small Anim Pract”, 1996, 37, 116-125.21.
- Bright J.M., Dentino M.: Indirect arterial blood pressure measurementin nonsedated Irish wolfhounds: reference values for the breed. „J Am Anim Hosp Assoc”, 2002, 38, 521-526, 22.
- Surman S. et al.: Arterial blood pressure, proteinuria, and renal histopathology in clinically healthy retired racinggreyhounds. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2012, 26, 1320-1329.
- Perez-Sanchez A.P. et al.: Obesity-hypertension and its relation to other diseases in dogs. „Vet Res Commun”, 2015, 39, 45-51.
- Schneider H.P., Truex R.C., Knowles J.O.: Comparative observati ons of thehearts of mongre l and greyhound dogs. „Anat Rec”, 1964, 149, 173-179, 32.
- Cox R.H., Peterson L.H., Detweiler D.K.: Comparison of arterial hemody-namics in the mongrel dog and the racing greyhound. „Am J Physiol”,1976, 230, 211-218.
- Acierno M.J. et al.: ACVIM consensus statement: Guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2018 Nov, 32 (6), 1803-1822.
lek. wet. Anna Kuziemska-Raczyńska
Katedra Biostruktury i Fizjologii Zwierząt
Wydział Medycyny Weterynaryjnej
Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu
ul. Norwida 31, 50-365 Wrocław
Galeria
Mogą zainteresować Cię również
Znajdź swoją kategorię
2641 praktycznych artykułów - 324 ekspertów - 22 kategorii tematycznych
Weterynaria w Terenie

Niezakaźne przyczyny chorób kończyn u świń
Problem kulawizn u loch Kulawizny u loch są, tuż po problemach w rozrodzie, najważniejszą przyczyną brakowań loch z dalszej hodowli. Najwięcej przypadków obserwuje się w okresie od odsadzenia do momentu porodu. Bardzo często schorzenia kończyn są rejestrowane u pierwiastek lub u loch po drugim porodzie, a więc w okresie, kiedy wchodzą one w najbardziej wydajny […]

Posocznica cieląt wywołana przez E. coli. Kolisepticemia
Zapobieganie W przypadku zachorowań na kolisepticemię należy brać pod uwagę przede wszystkim dwa czynniki: niski poziom immunoglobulin w surowicy krwi oraz system odchowu cieląt sprzyjający zakażeniom patogennymi szczepami E. coli (14, 17, 18). Wiele czynników ma wpływ na transfer immunoglobulin siarowych. Jednak najważniejszą rolę odgrywają czas, w jakim zostanie podana siara po urodzeniu, oraz ilość […]

Niezakaźne przyczyny chorób kończyn u świń
Problem kulawizn u loch Kulawizny u loch są, tuż po problemach w rozrodzie, najważniejszą przyczyną brakowań loch z dalszej hodowli. Najwięcej przypadków obserwuje się w okresie od odsadzenia do momentu porodu. Bardzo często schorzenia kończyn są rejestrowane u pierwiastek lub u loch po drugim porodzie, a więc w okresie, kiedy wchodzą one w najbardziej wydajny […]

Kiedy warto zlecić rozmaz krwi u koni?
Preanalityka Warunkiem wstępnym do otrzymania diagnostycznego wyniku rozmazu krwi jest jego prawidłowe wykonanie. Najważniejszą zasadą jest wykonanie rozmazu ze świeżej próbki krwi – najlepiej od razu, a maksymalnie do 24 godzin od pobrania. W trakcie przechowywania już po kilku, kilkunastu godzinach komórki krwi podlegają degeneracji, która utrudnia lub uniemożliwia ich rzetelną ocenę morfologiczną. Należy zwrócić […]
Wskazówki na wypadek widocznego niepowodzenia terapii antybiotykowej. Kryteria skutecznej terapii oraz kluczowe pytania jako 5 kroków drzewa analitycznego
Czynniki powiązane z użyciem antybiotyku w terapii: Czy wybór antybiotyku opierał się na badaniach klinicznych i dodatkowych (diagnoza, antybiogram)? Sprawdź odpowiedź na pytanie 3. Farmakokinetyka/farmakodynamika wybranego antybiotyku? Koncentracja i czas działania antybiotyku w zakażonej tkance a efektywność w stosunku do czynnika bakteryjnego wywołującego chorobę (spektrum działania antybiotyku, wrażliwość z antybiogramu – odpowiedzi na pytanie 3.). […]

Czarno na białym – mastitis okiem praktyka – rozmowa z dr. n. wet. Sebastianem Smulskim
Rozmowa z dr. n. wet. Sebastianem Smulskim, pracownikiem Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczego w Poznaniu, specjalistą w dziedzinie profilaktyki i leczenia mastitis u krów, który w swoich badaniach zgłębia tematykę zapalenia gruczołu mlekowego u bydła, zarówno w aspekcie naukowym, jak i praktycznym. Większość zapaleń gruczołu mlekowego ma etiologię bakteryjną. Dlaczego, pomimo rozwoju mikrobiologii, medycyny weterynaryjnej i prowadzonych badań, […]

XVIII FORUM ZOOTECHNICZNO-WETERYNARYJNE: NOWE HORYZONTY W ROZRODZIE ZWIERZĄT
Na Uniwersytecie Przyrodniczym w Poznaniu w dniach 18-19 kwietnia br. odbyło się XVIII Forum Zootechniczno-Weterynaryjne pod hasłem „Rozród zwierząt w dobie selekcji genomowej”. To wydarzenie zgromadziło liczne grono lekarzy weterynarii oraz hodowców, by omówić najnowsze osiągnięcia w dziedzinie hodowli i rozrodu zwierząt. Organizacja Forum była wspólnym przedsięwzięciem Poznańskiego Koła Polskiego Towarzystwa Zootechnicznego, Wielkopolskiego Oddziału Polskiego […]