Farmakoterapia bólu neuropatycznego u psów i kotów
Piśmiennictwo
- Szczudlik A., Dobrogowski J., Wordliczek J., Stępień A., Krajnik M., Leppert W., Woroń J., Przeklasa-Muszyńska A., Kocot-Kępska M., Zajączkowska R., Janecki M., Adamczyk A., Malec-Milewska M.: Rozpoznanie i leczenie bólu neuropatycznego: przegląd piśmiennictwa i zalecenia Polskiego Towarzystwa Badania Bólu i Towarzystwa Neurologicznego – część pierwsza. „Ból”, 2014, 15, 2, 8-18, DOI: 10.5604/1640324x.1115164.
- Bennett M.I., Rayment C., Hjermstad M., Aass N., Caraceni A., Kaasa S.: Prevalence and aetiology of neuropathic pain in cancer patients: A systematic review. „Pain”, 2012, 153, 359-365.
- Boldt I., Eriks-Hoogland I., Brinkhof M.W., de Bie R., Joggi D., von Elm E.: Non-pharmacological interventions for chronic pain in people with spinal cord injury. „Cochrane Database Syst Rev”, 2014, 11, CD009177. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009177.
- Gilron I., Baron R., Jensen T.: Neuropathic pain: principles of diagnosis and treatment. „Mayo Clin Proc”, 2015, 4, 532-45. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.01.018.
- Woolf C.J.: What is this thing called pain? „J Clin Invest”, 2010, 120 (11), 3742-4. DOI: 10.1172/JCI45178 (Epub 2010 Nov 1).
- Ruel H.L.M., Watanabe R., Evangelista M.C., Beauchamp G., Auger J.P., Segura M., Steagall P.V.: Pain burden, sensory profile, and inflammatory cytokines of dogs with naturally occurring neuropathic pain treated with gabapentin alone or with meloxicam. 2020, 30, 15 (11), e0237121. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237121 (eCollection 2020).
- Gilron I., Jensen T.S., Dickenson A.H.: Combination pharmacotherapy for management of chronic pain: from bench to bedside. „Lancet Neurol”, 2013 Nov, 12 (11), 1084-95. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70193-5. Epub 2013 Sep 25.
- Finnerup N.B., Sindrup S.H., Jensen T.S.: The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. „Pain”, 2010, 150 (3), 573-581. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.06.019.
- Harriott B.S., Gold M.S.: Contribution of primary afferent channels to neuropathic pain. „Curr Pain Headache Rep”, 2009, 13, 197-207.
- Xua Q., Yaksh T.L.: A brief comparison of the pathophysiology of inflammatory versus neuropathic pain. „Curr Opin Anaesthesiol”, 2011, 24, 400-407.
- Park J.S., Voitenko N., Petralia R.S. et al.: Persistent inflammation induces GluR2 internalization via NMDA receptor – triggered PKC activation in dorsal horn neurons. „J Neurosci”, 2009, 29, 3206-3219.
- Liu F., Yuan H.: Role of glia in neuropathic pain. ”Front Biosci (Landmark Ed)”, 2014, 19, 798-807. DOI: 10.2741/4247.
- Olmarker K., Rydevik B.: Selective inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents nucleus pulposus-induced thrombus formation, intraneural edema, and reduction of nerve conduction velocity: possible implications for future pharmacologic treatment strategies of sciatica. „Spine”, 2001, 26, 863-9. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00007.
- Quintao N.L., Balz D., Santos A.R., Campos M.M., Calixto J.B.: Long-lasting neuropathic pain induced by brachial plexus injury in mice: role triggered by the pro-inflammatory cytokine, tumour necrosis factor alpha. „Neuropharmacology”, 2006, 50, 614-20. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.11.007.
- Wordliczek J., Zajączkowska R., Leppert W.: Farmakoterapia bólu neuropatycznego. „Medycyna Paliatywna w Praktyce”, 2017, 11, 262.
- Monteiro B.P., Lascelles B.D.X., Murrell J., Robertson S., Steagall P.V.M., Wright B.: 2022 WSAVA guidelines for the recognition, assessment, and treatment of pain. „Journal of Small Animal Practice”, 2022.
- Attal N., Bouhassira D.: Pharmacotherapy of neuropathic pain: which drugs, which treatment algorithms? „Pain”, 2015, 156, 1, S104-S114, DOI: 10.1097/01.j.pain.0000460358.01998.15 (Indexed in Pubmed: 25789426).
- Cashmore R.G., Harcourt-Brown T.R., Freeman P.M., Jeffery N.D., Granger N.: Clinical diagnosis, and treatment of suspected neuropathic pain in three dogs. „Aust Vet J”, 2009, 87, 45-50. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.2008. 00379.x.
- Kukanich B., Cohen R.L.: Pharmacokinetics of oral gabapentin in greyhound dogs. „Vet J”, 2011, 187 (1), 133-135.
- Siao K.T., Pypendop B.H., Ilkiw J.E.: Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in cats. „Am J Vet Res”, 2010, 71 (7), 817-821.
- Bockbrader H.N., Wesche D., Miller R. et al.: A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. „Clin Pharmacokinet”, 2010, 49 (10), 661-669.
- Gidal B.E., Maly M.M., Kowalski J.W. et al.: Gabapentin absorption: effect of mixing with foods of varying macronutrient composition. „Ann Pharmacother”, 1998, 32, 405-409.
- Crociolli G.C., Cassu R.N., Barbero R.C. et al.: Gabapentin as an adjuvant for postoperative pain management in dogs undergoing mastectomy. „J Vet Med Sci”, 2015, 77, 1011-1015.
- Wagner A.E., Mich P.M., Uhrig S.R., Hellyer P.W.: Clinical evaluation of perioperative administration of gabapentin as an adjunct for postoperative analgesia in dogs undergoing amputation of a forelimb. „J Am Vet Med Assoc”, 2010, 236 (7), 751-6. DOI: 10.2460/javma.236.7.751.
- Salazar V., Dewey C.W., Schwark W., Badgley B.L., Gleed R.D., Horne W. et al.: Pharmacokinetics of single-dose oral pregabalin administration in normal dogs. „Vet Anaesth Analg”, 2009, 36, 574-80. DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2009. 00486.x.
- Esteban M.A., Dewey C.W., Schwark W.S., Rishniw M., Boothe D.M.: Pharmacokinetics of Single-Dose Oral Pregabalin Administration in Normal Cats. „Frontiers in Veterinary Science”, 2018, 5, 136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2018.00136.
- Lamminen T., Doedée A., HyttiläHopponen M., Kaskinoro J.: Pharmacokinetics of single and repeated oral doses of pregabalin oral solution formulation in cats. „Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics”, 2022, 45, 385-391. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.13061.
- Thoefnera M.S., Skovgaardb L.T., McEvoya F.J., Berendta M., Bjerrum O.J.: Pregabalin alleviates clinical signs of syringomyelia-related central neuropathic pain in Cavalier King Charles Spaniel dogs: a randomized controlled trial. „Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia”, 2020, 47, 238e248. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaa.2019.09.007238.
- Chew D.J., Buffington C.A., Kendall M.S., DiBartola S.P., Woodworth B.E.: Amitriptyline treatment for severe recurrent idiopathic cystitis in cats. „J Am Vet Med Assoc”, 1998, 213 (9), 1282-6.
- Kukes V.G., Kondratenko S.N., Savelyeva M.I., Starodubtsev A.K., Gneushev E.T.: Experimental and clinical pharmacokinetics of amitryptiline: comparative analysis. „Bull Exp Biol Med”, 2009, 147, 434-7. DOI: 10.1007/s10517-009-0520-4.
- Monteiro B.P., de Lorimier L.P., Moreau M., Beauchamp G., Blair J., Lussier B., Pelletier J.P., Troncy E.: Pain characterization and response to palliative care in dogs with naturally occurring appendicular osteosarcoma: An open label clinical trial. „PLoS One”, 2018, 13 (12): e0207200. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207200.
- Steagall P., Robertson S.A., Taylor P.: Feline Anesthesia and Pain Management. WILEY Blackwell, 2017.
- Perez Jimenez T.E., Mealey K.L., Grubb T.L., Greene S.A., Court M.H.: Tramadol metabolism to O-desmethyl tramadol (M1) and N-desmethyl tramadol (M2) by dog liver microsomes: Species comparison and identification of responsible canine cytochrome P-450s (CYPs). ”Drug Metab Dispos”, 2016, 44 (12), 1963-1972./[published correction appears in] „Drug Metab Dispos”, 2017, 45 (7), 706. DOI: 10.1124/dmd.116.071902.
- Lavand’homme P., Thienpont E.: Pain after total knee arthroplasty: a narrative review focusing on the stratification of patients at risk for persistent pain. „Bone Joint J”, 2015, 97-B, 45-8. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.97B10.36524.
- Lyons P.J., Rivosecchi R.M., Nery J.P., Kane-Gill S.L.: Fentanyl-induced hyperalgesia in acute pain management. „J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother”, 2015, 29 (2), 153-60. DOI: 10.3109/15360288.2015.1035835. PMID: 26095487.
- Santonocito C., Noto A., Crimi C., Sanfilippo F.: Remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia: current perspectives on mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. „Local Reg Anesth.”, 2018, 11, 15-23. DOI: 10.2147/LRA.S143618 (Published 2018 Apr 9).
- KuKanich B., Papich M.G.: Pharmacokinetics of tramadol and the metabolite O-desmethyltramadol in dogs. „J Vet Pharmacol Ther”, 2004, 27, 239-246.
- Monteiro B.P., Klinck M.P., Moreau M., Guillot M., Steagall P.V., Pelletier J.P., Martel-Pelletier J., Gauvin D., Del Castillo J.R., Troncy E.: Analgesic efficacy of tramadol in cats with naturally occurring osteoarthritis. „PLoS One”, 2017, 12 (4), e0175565. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175565.
- Guedes A.G.P., Meadows J.M., Pypendop B.H., Johnson E.G.: Evaluation of tramadol for treatment of osteoarthritis in geriatric cats. „J Am Vet Med Assoc”, 2018 Mar 1, 252 (5), 565-571. doi: 10.2460/javma.252.5.565. PMID: 29461159.
- Domínguez-Oliva A., Casas-Alvarado A., Miranda-Cortés A.E., Hernández-Avalos I.: Clinical pharmacology of tramadol and tapentadol, and their therapeutic efficacy in different models of acute and chronic pain in dogs and cats. „J Adv Vet Anim Res”, 2021, 8 (3), 404-422. DOI: 10.5455/javar.2021.h529 (Published 2021 Sep 19).
- Siao K.T., Pypendop B.H., Stanley S.D.: Pharmacokinetics of amantadine in cats. „J Vet Pharmacol Ther”, 2011, 34, 599-604.
- Lascelles B.D., Gaynor J.S., Smith E.S. et al.: Amantadine in a multimodal analgesic regimen for alleviation of refractory osteoarthritis pain in dogs. „J Vet Intern Med”, 2008, 22 (1), 53-59.
- Cimino Brown D.: Resiniferatoxin: The Evolution of the „Molecular Scalpel” for Chronic Pain Relief. „Pharmaceuticals”, 2016, 9 (3), 47.
- Koppel B.S., Brust J.C., Fife T., Bronstein J., Youssof S., Gronseth G. et al.: Systematic review: efficacy and safety of medical marijuana in selected neurologic disorders: report of the guideline development subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. „Neurology”, 2014, 82, 1556-63. DOI: 10.1212/ WNL.0000000000000363.
- Tauben D.: Nonopioid medications for pain. „Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am”, 2015, 26, 219-48. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmr.2015.01.005.
- Karlik W.: Co lekarz weterynarii powinien wiedzieć o produktach z konopi. „Magazyn Weterynaryjny”, 2020.
- Pascual D. et al.: A cannabinoid agonist, WIN 55,212-2, reduces neuropathic nociception induced by paclitaxel in rats. „Pain”, 2005, 118, 1-2.
- Xiong W. et al.: Administration of cannabidiol (indirect antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists) significantly suppressed chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in rodents. 2012.
- Gamble L.J., Boesch J.M., Frye C.W., Schwark W.S., Mann S., Wolfe L., Brown H., Berthelsen E.S., Wakshlag J.J.: Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Clinical Efficacy of Cannabidiol Treatment in Osteoarthritic Dogs. „Front Vet Sci”, 2018, 5, 165. DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00165.
- Wilson-Morkeh H., Al-Abdulla A., Sien L., Mohamed H., Youngstein T.: Important drug interactions exist between cannabidiol oil and commonly prescribed drugs in rheumatology practice. „Rheumatology”, 2020, 59, 1, 249-251. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez304.
- della Rocca G., Gamba D.: Chronic Pain in Dogs and Cats: Is There Place for Dietary Intervention with Micro-Palmitoylethanolamide? „Animals”, 2021, 11 (4), 952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11040952.
- 52. Enomoto M., Mantyh P.W., Murrell J., Innes J.F., Lascelles B.D.X.: Anti-nerve growth factor monoclonal antibodies for the control of pain in dogs and cats. „Vet Rec”, 2019, 184 (1), 23. DOI: 10.1136/vr.104590.
- Krautmann M., Walters R., Cole P., Tena J., Bergeron L.M., Messamore J., Mwangi D., Rai S., Dominowski P., Saad K., Zhu Y., Guillot M., Chouinard L.: Laboratory safety evaluation of bedinvetmab, a canine anti-nerve growth factor monoclonal antibody, in dogs. „The Veterinary Journal”, 2021, 276, 105733. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2021.105733.
- Goich M., Bascuńán A., Faúndez P., Valdés A.: Multimodal analgesia for treatment of allodynia and hyperalgesia after major trauma in a cat. „JFMS Open Rep”, 2019, 5 (1), 2055116919855809. DOI: 10.1177/2055116919855809 (Published 2019 Jun 18).
lek. wet. Zofia Fraś
Przychodnia Weterynaryjna „BIAŁOBRZESKA”
ul. Częstochowska 20 02-344 Warszawa
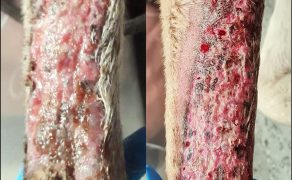
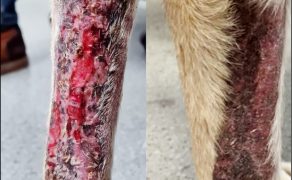
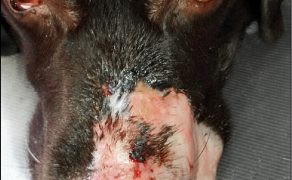
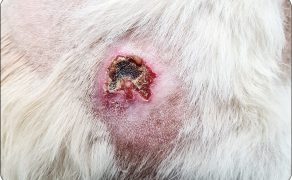
Galeria
Mogą zainteresować Cię również
110
ALGORYTMY
POSTĘPOWANIA
w weterynarii
POSTĘPOWANIA
w weterynarii