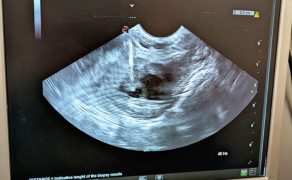
Profilaktyka mastitis w okresie zasuszenia krów
Piśmiennictwo
- Accorsi P.A., Pacioni B., Pezzi C., Forni M., Flint D.J., Seren E.: Role of prolactin, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor 1 in mammary gland involution in the dairy cow. „J Dairy Sci”, 2002, 85, 507-513.
- Blowey R., Edmondson P.: Mastitis Control in dairy herds. CABI, 2010.
- Bushe T., Oliver S.P.: Natural protective factors in bovine mammary secretions following different methods of milk cessation. „J Dairy Sci”, 1987, 70, 696-704.
- Cohick W.S.: Role of the insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in lactation. „J Dairy Sci”, 1998, 81, 1769-1777.
- Dingwell R.T., Leslie K.E., Schukken Y.H., Sargeant J.M., Timms L.L., Duffield T.F., Keefe G.P., Kelton D.F., Lissemore K.D., Conklin J.: Association of cow and quarter-level factors at drying-off with new intramammary infections during the dry period. „Prev Vet Med”, 2004, 63, 75-89.
- Farm Animal Welfare Council FAWC updates the Five Freedoms. „Veterinary Record”, 1992, 17, 357.
- Jerry D.J., Dickinson E.S., Roberts A.L., Said T.K.: Regulation of apoptosis during mammary involution by the p53 tumor suppressor gene. „J Dairy Sci”, 2002, 85, 1103-1110.
- Jorstand A., Farver B.T., Riemann H.: Teat canal diameter and other cows factors with possible influence on somatic cell counts in cow [...]
Ten materiał dostępny jest tylko dla użytkowników
którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
którzy są subskrybentami naszego portalu.
Wybierz pakiet subskrypcji dla siebie
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!
i ciesz się dostępem do bazy merytorycznej wiedzy!
Masz aktywną subskrypcję?
Nie masz jeszcze konta w serwisie? Dołącz do nas
Mogą zainteresować Cię również
107
ALGORYTMY
POSTĘPOWANIA
w weterynarii
POSTĘPOWANIA
w weterynarii